How Can the Circular Economy Play a Part in A Sustainable Future?
1. Circular Economy
The circular economy represents a transformative approach to production and consumption, emphasizing sustainability and resource efficiency. It promotes the concepts of sharing, leasing, reusing, repairing, refurbishing, and recycling to extend the lifespan of products and materials. This departure from the linear economic model, which revolves around a take-make-consume-throw-away cycle, aims to minimize waste and keep materials in circulation through recycling, ultimately creating additional value. It also challenges the practice of planned obsolescence, where products are intentionally designed with limited lifespans to drive repeat purchases. The European Parliament has recognized the importance of addressing planned obsolescence as part of the circular economy paradigm, signaling a broader global shift towards a more sustainable and responsible economic model.
2. Sustainable Development
As defined by the International Institute of Sustainable Development, sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. The circular economy is intricately linked to sustainable development by promoting resource efficiency, achieving zero waste, and fostering economic growth while minimizing environmental impact, aligning with the broader goals of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development.
3. Circular Economy Market Insights
The global circular economy market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 10.5% from 2023 to 2028. Many market drivers affect the growth of the circular economy market positively. Increasing awareness of environmental issues, such as climate change, resource depletion, and pollution, has increased demand for sustainable practices, driving the adoption of circular economy principles. Governments and international organizations have established rules and regulations to encourage using circular economy methods. These policies include incentives for recycling, waste reduction targets, and initiatives to promote sustainable consumption and production. Businesses are learning that adopting circular economy principles may result in cost savings through better utilization of resources, decreased waste management expenses, and greater efficiency in operations. Consumer tastes are evolving toward items made sustainably and with a low environmental effect. This has pushed businesses to adopt circular economy principles to meet the growing demand for eco-friendly products.
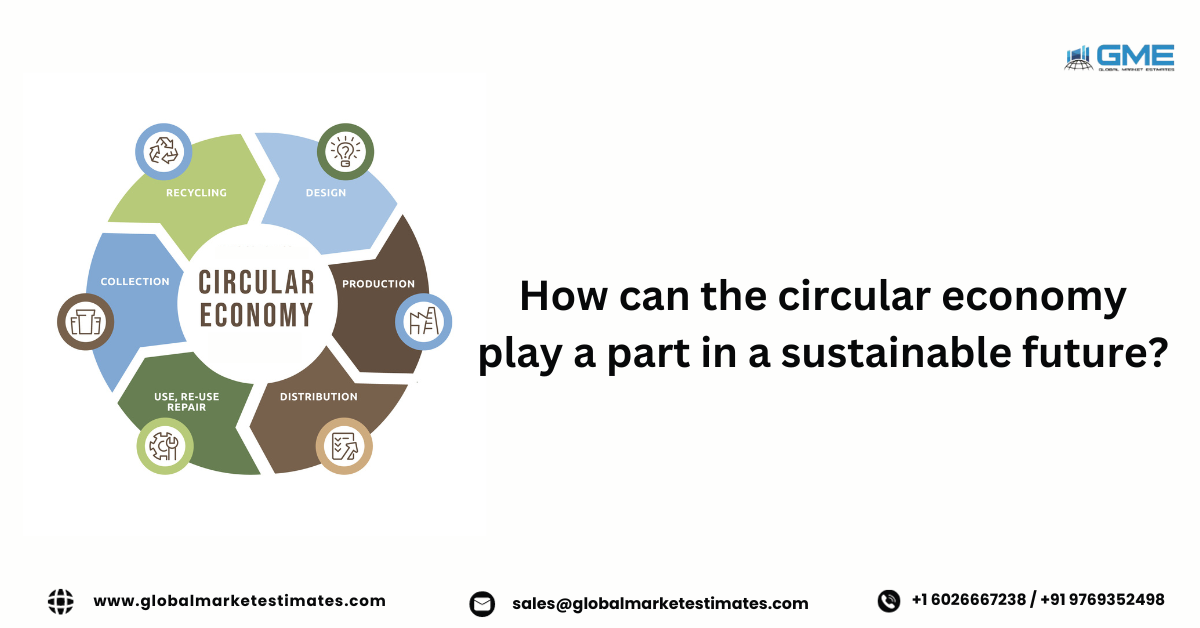
4. Components of Circular Economy
A circular economy optimizes supply chains to reduce resource consumption, minimize waste, and encourage recycling and reuse. Effective waste management systems are crucial for material recovery and reuse. Sustainable innovation is central, focusing on eco-friendly practices and recyclable materials. Circular economy principles encourage businesses to adopt sustainable business models, prioritizing product longevity, sharing, and remanufacturing, promoting sustainable practices throughout the value chain.
5. Impact of Circular Economy on the Future
A circular economy holds the potential to significantly shape the future by fostering sustainable and resilient economic systems. Its impact is multifaceted, including reduced resource depletion, minimized waste generation, increased job opportunities in green technology sectors, and heightened innovation in sustainable technologies. Additionally, it can contribute to mitigating climate change, enhancing energy efficiency, and fostering a more equitable and inclusive global economy, ultimately paving the way for a more sustainable and prosperous future for generations to come.
6. Market Players
Key players operating in the global circular economy market include Adidas AG, Amazon, Apple Inc., BMW, Cisco Systems, Danone, Dell Technologies, Dow Chemical Company, Ford Motor Company, General Motors, H&M, HP Inc., IBM Corp., IKEA, Inditex, L'Oréal, Nestlé, Panasonic Corporation, Zara SA, Philips, Procter & Gamble, Samsung Electronics, Schneider Electric, Siemens, Sony Group Corporation, Tesla Inc., Toyota Motor Corporation, Unilever, Veolia, and Walmart, among others.
7. Achieving Sustainability Through Circular Economy
Achieving sustainability through the circular economy involves a multifaceted approach. This includes redesigning products to prioritize durability, reparability, and recyclability, optimizing resource efficiency through energy-saving technologies and renewable resources, implementing robust waste reduction and recycling systems, fostering collaborative partnerships among stakeholders for circular supply chains and sustainable business models, and raising consumer awareness to encourage responsible consumption practices like product sharing and repair. By adopting these strategies, societies can transition towards more sustainable practices, reducing environmental impact and preserving natural resources for future generations.
8. Circular Economy in Different Regions
Many countries are trying to achieve a circular economy to grow more sustainably. They have constructed laws and special departments which are dedicated to this purpose. The sustainable development goals (SDGs) further spur the countries to be sustainable in the future. The following is a short list of countries actively trying to achieve sustainability through a circular economy.
- India: The Circular Economy Cell (CE Cell) was established in September 2022 at NITI Aayog to focus on the Circular Economy. It has finalized 10 sectoral action plans for implementation by various Ministries/Departments. The Cell coordinates with MoRTH to operationalize the Vehicle Scrapping program and develops strategies for scrapping unfit and old vehicles. The upcoming financial year aims to prepare a comprehensive Mission Document, develop an interactive Dashboard, and engage with states.
- Netherlands: The Dutch government is working with various organizations to achieve a circular economy by 2050. The National Programme on Circular Economy 2023-230 aims to reduce raw material usage, substitute sustainably produced, extend product life, and recycle materials and raw materials. The programme includes measures for specific product groups and focus areas like education, procurement, and business models. The transition requires systemic changes in Europe and worldwide, with the Netherlands being a Platform for Accelerating the Circular Economy (PACE) member.
- Japan: The Act on the Promotion of Resource Circulation for Plastics was enacted in Japan in April 2022 to improve plastic circulation. The regulation covers the cradle-to-cradle supply chain, implementing measures at design, retail, service, and disposal stages. It aims to reduce single-use plastic use, encourage efficient recycling, and accelerate collaboration across supply chain partners.
9. Conclusion
In conclusion, the integration of circular economy principles holds immense promise in shaping a sustainable future for our planet. The circular economy presents a viable pathway towards a more sustainable and resilient global economy by fostering innovative product design, optimizing resource efficiency, and prioritizing waste reduction and recycling. Through collaborative partnerships and heightened consumer awareness, the transition towards circular practices can catalyze a paradigm shift in production and consumption patterns, practicing environmental conservation and promoting the preservation of natural resources. Embracing the circular economy is not only crucial for addressing the challenges of resource scarcity and climate change but also for fostering a more equitable and prosperous future for generations to come.